|
| Menüeintrag |
|---|
| Arch → Space |
| Arbeitsbereich |
| Arch |
| Standardtastenkürzel |
| S P |
| Siehe auch |
| None |
Description
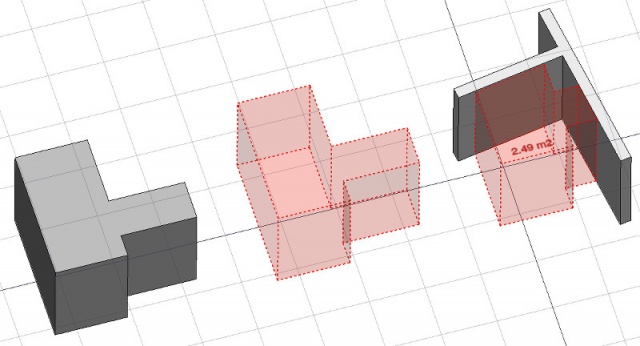
The Space tool allows you to define an empty volume, either by basing it on a solid shape, or by defining its boundaries, or a mix of both. If it is based solely on boundaries, the volume is calculated by starting from the bounding box of all the given boundaries, and subtracting the spaces behind each boundary. The space object always defines a solid volume. The floor area of a space object, calculated by intersecting a horizontal plane at the center of mass of the space volume, can also be displayed, by setting the display mode of the space object to "detailed".
In the above image, a space object is created from an existing solid object, then two wall faces are added as boundaries, and the display mode is set to "detailed" to show the floor area.
Anwendung
- Select an existing solid object, or faces on boundary objects
- Press the
 Arch Space button, or press S, P keys
Arch Space button, or press S, P keys
Properties
- DATABase: The base object, if any (must be a solid)
- DATABoundaries: A list of optional boundary elements
Scripting
The space tool can be used in python scripts and macros by using the following function:
makeSpace(objects)
- Creates a space object from the given objects.
- Objects can be one document object, in which case it becomes the base shape of the space object, or a list of selection objects as returned by FreeCADGui.Selection.getSelectionEx(), or a list of tuples (object, subobjectname).
- Returns the newly created space object.
Example:
import FreeCAD, Arch, Part
b = Part.makeBox(2,2,2)
FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Feature","Box").Shape=b
sp = makeSpace([FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.Box])
After a space object is created, selected faces can be added to it with the following function:
import FreeCADGui Arch.addSpaceBoundaries(sp, FreeCADGui.Selection.getSelectionEx())
Boundaries can also be removed with:
Arch.removeSpaceBoundaries(sp, FreeCADGui.Selection.getSelectionEx())
Limitations
- Not available below FreeCAD version 0.14
- The boundaries properties is currently not editable via GUI
- See the forum announcement