Here the project plan for the Assembly modul as part of the Development roadmap
Contents
Purpose and principles
This is a software development project aimed to implement a Assembly and product creation capabilities. Its about implementing some core features into the CAD modules of FreeCAD, Part and Assembly.
The development steps are planed here and tracked in the Issue tracking system to get a well formed change log: Issue tracker
Outcome
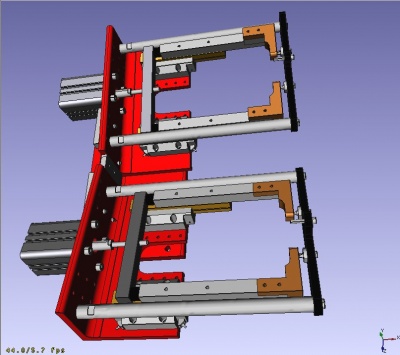
Aim of the project is to enable FreeCAD accomplish a design task like this one:
This will be achived by using the Assembly to put all the different kind of parts together with constraints and stay as close as possible to the ISO 10303 specification to allow easy model exchange.
Another aim is to utilize ODE for kinematics.
Brainstorming
Multi model
A key feature to real world designs is the ability to split a design into handleable pieces. Its impossible to work on all aspects of a design at the same time or alone. That is true for the geometry and also for engineering tasks like FEM or CAM. There for FreeCAD need the ability to split models. That opens some possibilities:
- Late loading - Only need resources like Graphics and main memory for the piece you work on.
- Concurrent engineering - allows many people to work on the same design
- Fine grained Version control - better control over various aspects of the design
- and many more....
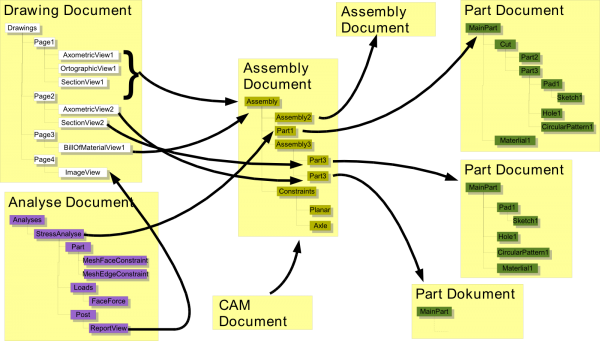
A multi model design could look like that:
Project management
Multi model means a lot of files belonging to one project, most likely under a common directory. A project file and a project browser can help organizing the files. Also it can save additional information about the project or a project website.
1. Two modes, the "Simple" and the "Project" mode. Simple mean only one document and all the assemblies and parts go in one document. If a Project is opened or created FreeCAD is in project mode.
2. Projects. The position of the FCPrj file on the drive defines a root directory. All Files below this dir are defined with relative paths to the root dir. A additional view on the left side will hold the ProjectExplorer which shows the dir tree with the handled files. This root dir is also used as root for a SVN sand box, which allows later ease sharing and Version control. External references (towards a dir outside root, a sever share or a web resource) will handled and showed separably in the ProjectExplorer (one pseudo dir for each file server or web server). This makes it possible to get a fast overview about external references and re-route them.
Copyright
Now copyright of 3D models is a interesting field. 3D models do fall under the copyright. The copyright falls to the creator of the model. Its only possible to protect the shape, which is represented by the model, by a patent or a design patent (US). But patents cover only the creation of a physical part to earn money. As an example the Microsoft Mouse design patent.
So we have to remember the creator (copyright holder) and any kind of license for each model/product/file of a design. For the license I would use the CC type licenses. http://creativecommons.org/
Abbreviation Keys for CC licenses:
- BY = Attribution only
- BY-ND = Attribution-NoDerivatives
- BY-NC-ND = Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives
- BY-NC = Attribution-NonCommercial
- BY-NC-SA = Attribution-NonCommercial- ShareAlike
- BY-SA = Attribution-ShareAlike
- PD = Dedicated to or marked as being in the public domain via one of our public domain tools, or other public domain work; adaptations of works in the public domain may be built upon and licensed by the creator under any license terms desired
Additional a URL link to the full license document (in case of custom licenses)
ISO 10303
The ISO 10303 (STEP) is very important in this field. Its the only good standardized and widely discussed and recognized definition of product structures I know of.
Here some links with info:
- ISO 10303 on Wikipedia
- WikiStep.org with a lot of basic info but mostly toward STEP-NC
- The product structure in STEP
- Some examples about STEP
- ISO 10303-11 about the modeling language (EXPRESS)
- A Wikipedia article about product modeling
- Overview of Part 41 -- Fundamentals of Product Description and Support
- Overview of Part 44 (edition 2) -- Product Structure Configuration
- Examples of small AP 214 files
Assembly constraints
An important role in building up large models and products take the assembly constraints, which formulate certain rules how parts assemble a product. Mainly these are Fix, FaceToFace, Angle, Offset and some kind of pattern instantiation. This constraints need a specialized solver to keep them up if the parts change. This solver is fundamentally different to the Sketch solver. I think we have to go for a graph based approach on this...
Kinematics
A further step would be to use ODE, or similar libs, to put the parts and the assembly constraints together to do a kinematic simulation of machines. That would allow checking for collisions and exploring the conditions of a mechanical system.
Revision control
An important point is the version control and distributed development. With multi model design we are able to split designs in smaller pieces and can distribute work among a team. For a software developer "distributed" and "Version" sounds familiar, so why not use a DVCS. A good comparison is here.
Since we deal with big data, and data which can not be easily diffed, we are limited to those which use the snapshot persistence model. Any system storing just diffs will have grave problems with our data (personally tested with Mercurial and Catia files). After sorting out commercial and non-free, basically only Git and SVN remains.
Using Git for the task leaves us with two big frontiers:
- Git is very complicated; Branching merging and tagging along a non linear development path let alone merging with remote repositories (push, pull)
will put a lot of complexity in that matter. To hide it from the user will be a challenging task.
- Git allow Merge and Diff handlers for certain file types; We need one for .fcstd. This handler has to examine two FreeCAD
documents and show and merge differences in the objects, features and parameters. Also not easy.
But using git would open a lot of possibilities even high class PLM system would dream of...
Organizing
Here some development task needed for a decent Assembly/Product design:
Infrastructure
The assembly will demand some changes in the base system and infrastructure layer of FreeCAD.
Multi model
Multi-Model was in mind from the beginning of FreeCADs design. There fore we have a multi document interface and can load unlimited documents. But we need to upgrade especially the 3D-Viewer to handle showing more the one document in its view (Part-Trees).
Part-Trees
Since in Assembly the composition of parts and sub-assemblies is the main workflow, the tools to stack (group) Parts in a tree have to be implemented. Unlike a DocumentObjectGroup the Assembly group has to deal with visibility and placement of the children. Best done by stacking ViewProvider on each other. That need a kind of ClaimChildren() interface to the ViewProviders.
Unified Drag/Drop/Copy/Paste interface
A interface allow ViewProvider and Workbenches full control about Drag/Drop/Copy/Paste operations in the tree or the 3D view.
External resources
Handling of doped links (from internal or external browsers). Means loading resources over (potential) slow connections (http).
Material
Describing material and its properties is a vital part of a CAD/CAE system. Material has a lot of properties and names heavily dependent on the field its use. E.g. FEM and mechanical engineering have different frameworks and standards to describe Material.
For the Material description a special article is made: Material
Object model
Class tree to deal with concepts needed. References, interfaces, document links, views, compounds, constraints, configurations, and many more...
STEP check loop
Implementing a first STEP importer for more then geometry and color to check if the object model holds for a wider usage.
Assembly constraint solver
Define a interface to a assembly constraint solver, very similar to the Sketcher solver interface.
Physics simulation interface
Interface to allow a (external) (multi)physics simulation software to take control over the positioning of the Parts of a assembly. This would allow to use "bullet" or "ODE" to do kinematic tests and DMU.
Next actions
- Object model
- Wait for the 0.12 release branch happened