ドローイングモジュールを使うと3D作業物を紙の上に移すことができます。つまりモデルのビューを2Dウィンドウに表示し、図面にそのウィンドウを挿入するということです。例えば枠線、タイトル、ロゴマークが入ったシートに挿入し、最終的にそのシートを印刷することができます。ドローイングモジュールは現在も製作中で多かれ少なかれ技術面でのテスト段階にあります!
Contents
GUIツール
2D図面を作成、設定、エキスポートするためのツールです。
-
 スケーラブルベクターグラフィックを開く: SVGファイルとして保存されている図面を開きます
スケーラブルベクターグラフィックを開く: SVGファイルとして保存されている図面を開きます
-
 A3図面の新規作成: FreeCADのデフォルトのA3テンプレートから新しい図面を作成します
A3図面の新規作成: FreeCADのデフォルトのA3テンプレートから新しい図面を作成します
-
 ビューの挿入: アクティブな図面上に選択されたオブジェクトのビューを挿入します
ビューの挿入: アクティブな図面上に選択されたオブジェクトのビューを挿入します
-
 Annotation: Adds an annotation to the current drawing sheet
Annotation: Adds an annotation to the current drawing sheet
-
 Clip: Adds a clip group to the current drawing sheet
Clip: Adds a clip group to the current drawing sheet
-
 Open Browser: Opens a preview of the current sheet in the browser
Open Browser: Opens a preview of the current sheet in the browser
-
 Ortho Views: Automatically creates orthographic views of an object on the current drawing sheet
Ortho Views: Automatically creates orthographic views of an object on the current drawing sheet
-
 Symbol: Adds the contents of a SVG file as a symbol on the current drawing sheet
Symbol: Adds the contents of a SVG file as a symbol on the current drawing sheet
-
 Draft View: Inserts a special Draft view of the selected object in the current drawing sheet
Draft View: Inserts a special Draft view of the selected object in the current drawing sheet
-
 Spreadsheet View: Inserts a view of a selected spreadsheet in the current drawing sheet
Spreadsheet View: Inserts a view of a selected spreadsheet in the current drawing sheet
-
 図面の保存: 現在の図面をSVGファイルとして保存します
図面の保存: 現在の図面をSVGファイルとして保存します
- Project Shape: Creates a projection of the selected object (Source) in the 3D view.
Note The Draft View tool is used mainly to place Draft objects on paper. It has a couple of extra capabilities over the standard Drawing tools, and supports specific objects like Draft dimensions.
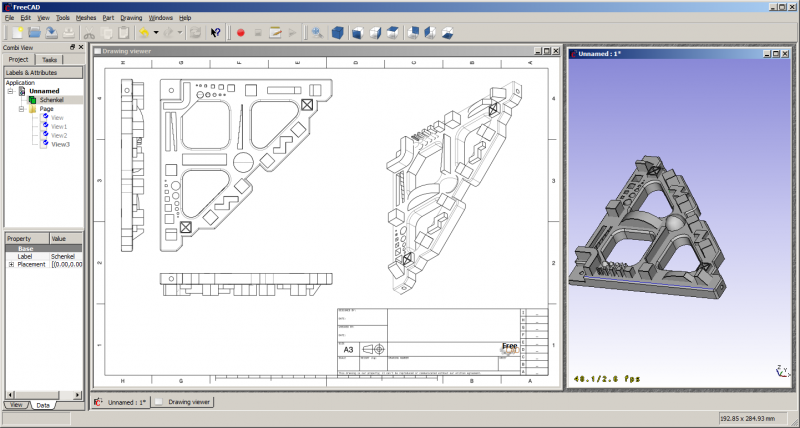
この画像を見るとドローイングモジュールの主要なコンセプトが見て取れます。ドキュメントには図面に引用したい形状オブジェクト(Schenkel)が入っています。さらに"Page"が作成されています。ページはテンプレートに基づいてインスタンス化されます。今回のケースでは"A3_Landscape"テンプレートです。テンプレートにはSVGドキュメントであなたが普段使っているページ枠、ロゴ、標準のプレゼンテーション資料規格を使うことができます。
このページには複数のビューを挿入することができます。各ビューはページ上での位置(X、Yプロパティ)、拡大率(スケールプロパティ)などをはじめとした属性情報を持っています。ページ、ビュー、参照しているオブジェクトが変化するとそのたびにページが再生成され、ページの表示が更新されます。
スクリプト処理
今のところエンドユーザー用の(GUI)ワークフローは非常に限定されたものしか用意されていません。APIはもっと充実しています。以下ではドローイングモジュールのスクリプト処理用APIをどう使うかの例を挙げていきます。
Here a script that can easily fill the Macro_CartoucheFC leaf FreeCAD A3_Landscape.
簡単な例
まずはパートモジュールとドローイングモジュールが必要です。
import FreeCAD, Part, Drawing
小さなサンプルパーツを作成します。
Part.show(Part.makeBox(100,100,100).cut(Part.makeCylinder(80,100)).cut(Part.makeBox(90,40,100)).cut(Part.makeBox(20,85,100)))
投影させます。G0はシャープな輪郭線、G1は連続線を意味します。
Shape = App.ActiveDocument.Shape.Shape [visibleG0,visibleG1,hiddenG0,hiddenG1] = Drawing.project(Shape) print "visible edges:", len(visibleG0.Edges) print "hidden edges:", len(hiddenG0.Edges)
Everything was projected on the Z-plane:
print "Bnd Box shape: X=",Shape.BoundBox.XLength," Y=",Shape.BoundBox.YLength," Z=",Shape.BoundBox.ZLength print "Bnd Box project: X=",visibleG0.BoundBox.XLength," Y=",visibleG0.BoundBox.YLength," Z=",visibleG0.BoundBox.ZLength
異なる投影ベクトル。
[visibleG0,visibleG1,hiddenG0,hiddenG1] = Drawing.project(Shape,App.Vector(1,1,1))
SVGに投影。
resultSVG = Drawing.projectToSVG(Shape,App.Vector(1,1,1)) print resultSVG
パラメトリックな方法
物体を作成します。
import FreeCAD
import Part
import Drawing
# Create three boxes and a cylinder
App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Box","Box")
App.ActiveDocument.Box.Length=100.00
App.ActiveDocument.Box.Width=100.00
App.ActiveDocument.Box.Height=100.00
App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Box","Box1")
App.ActiveDocument.Box1.Length=90.00
App.ActiveDocument.Box1.Width=40.00
App.ActiveDocument.Box1.Height=100.00
App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Box","Box2")
App.ActiveDocument.Box2.Length=20.00
App.ActiveDocument.Box2.Width=85.00
App.ActiveDocument.Box2.Height=100.00
App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Cylinder","Cylinder")
App.ActiveDocument.Cylinder.Radius=80.00
App.ActiveDocument.Cylinder.Height=100.00
App.ActiveDocument.Cylinder.Angle=360.00
# Fuse two boxes and the cylinder
App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Fuse","Fusion")
App.ActiveDocument.Fusion.Base = App.ActiveDocument.Cylinder
App.ActiveDocument.Fusion.Tool = App.ActiveDocument.Box1
App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Fuse","Fusion1")
App.ActiveDocument.Fusion1.Base = App.ActiveDocument.Box2
App.ActiveDocument.Fusion1.Tool = App.ActiveDocument.Fusion
# Cut the fused shapes from the first box
App.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Cut","Shape")
App.ActiveDocument.Shape.Base = App.ActiveDocument.Box
App.ActiveDocument.Shape.Tool = App.ActiveDocument.Fusion1
# Hide all the intermediate shapes
Gui.ActiveDocument.Box.Visibility=False
Gui.ActiveDocument.Box1.Visibility=False
Gui.ActiveDocument.Box2.Visibility=False
Gui.ActiveDocument.Cylinder.Visibility=False
Gui.ActiveDocument.Fusion.Visibility=False
Gui.ActiveDocument.Fusion1.Visibility=False
Pageオブジェクトを挿入し、テンプレートを代入
App.ActiveDocument.addObject('Drawing::FeaturePage','Page')
App.ActiveDocument.Page.Template = App.getResourceDir()+'Mod/Drawing/Templates/A3_Landscape.svg'
"Shape"オブジェクトのビューを作成。位置とサイズを定義してPageに代入
App.ActiveDocument.addObject('Drawing::FeatureViewPart','View')
App.ActiveDocument.View.Source = App.ActiveDocument.Shape
App.ActiveDocument.View.Direction = (0.0,0.0,1.0)
App.ActiveDocument.View.X = 10.0
App.ActiveDocument.View.Y = 10.0
App.ActiveDocument.Page.addObject(App.ActiveDocument.View)
同じオブジェクトに対して二つ目のビューを作成。ただし今回のビューは90度回転させます。
App.ActiveDocument.addObject('Drawing::FeatureViewPart','ViewRot')
App.ActiveDocument.ViewRot.Source = App.ActiveDocument.Shape
App.ActiveDocument.ViewRot.Direction = (0.0,0.0,1.0)
App.ActiveDocument.ViewRot.X = 290.0
App.ActiveDocument.ViewRot.Y = 30.0
App.ActiveDocument.ViewRot.Scale = 1.0
App.ActiveDocument.ViewRot.Rotation = 90.0
App.ActiveDocument.Page.addObject(App.ActiveDocument.ViewRot)
同じオブジェクトに対して三つ目のビューを作成。ただし等角図の方向を使用します。また隠れている線も表示させます。
App.ActiveDocument.addObject('Drawing::FeatureViewPart','ViewIso')
App.ActiveDocument.ViewIso.Source = App.ActiveDocument.Shape
App.ActiveDocument.ViewIso.Direction = (1.0,1.0,1.0)
App.ActiveDocument.ViewIso.X = 335.0
App.ActiveDocument.ViewIso.Y = 140.0
App.ActiveDocument.ViewIso.ShowHiddenLines = True
App.ActiveDocument.Page.addObject(App.ActiveDocument.ViewIso)
適当に何か変更して更新。更新処理によってビューとページが変化します。
App.ActiveDocument.View.X = 30.0 App.ActiveDocument.View.Y = 30.0 App.ActiveDocument.View.Scale = 1.5 App.ActiveDocument.recompute()
こまごまとした物へのアクセス
一つのビューからSVGの図を取得。
ViewSVG = App.ActiveDocument.View.ViewResult print ViewSVG
結果ページ全体を取得(ドキュメントのテンポラリフォルダ内の読み取り専用ファイル)。
print "Resulting SVG document: ",App.ActiveDocument.Page.PageResult file = open(App.ActiveDocument.Page.PageResult,"r") print "Result page is ",len(file.readlines())," lines long"
重要:ファイルを解放!
del file
独自のコンテンツを使用してビューを挿入。
App.ActiveDocument.addObject('Drawing::FeatureView','ViewSelf')
App.ActiveDocument.ViewSelf.ViewResult = """<g id="ViewSelf"
stroke="rgb(0, 0, 0)"
stroke-width="0.35"
stroke-linecap="butt"
stroke-linejoin="miter"
transform="translate(30,30)"
fill="#00cc00"
>
<ellipse cx="40" cy="40" rx="30" ry="15"/>
</g>"""
App.ActiveDocument.Page.addObject(App.ActiveDocument.ViewSelf)
App.ActiveDocument.recompute()
del ViewSVG
以下のような結果になります:
テンプレート
Drawing dimensions an tolerances are still under development but you can get some basic functionality with a bit of work.
First you need to get the gdtsvg python module from here (WARNING: This could be broken at any time!):
https://github.com/jcc242/FreeCAD
To get a feature control frame, try out the following:
import gdtsvg as g # Import the module, I like to give it an easy handle
ourFrame = g.ControlFrame("0","0", g.Perpendicularity(), ".5", g.Diameter(), g.ModifyingSymbols("M"), "A",
g.ModifyingSymbols("F"), "B", g.ModifyingSymbols("L"), "C", g.ModifyingSymbols("I"))
Here is a good breakdown of the contents of a feature control frame: http://www.cadblog.net/adding-geometric-tolerances.htm
The parameters to pass to control frame are:
- X-coordinate in SVG-coordinate system (type string)
- Y-coordinate in SVG-coordinate system (type string)
- The desired geometric characteristic symbol (tuple, svg string as first, width of symbol as second, height of symbol as third)
- The tolerance (type string)
- (optional) The diameter symbol (tuple, svg string as first, width of symbol as second, height of symbol as third)
- (optional) The condition modifying material (tuple, svg string as first, width of symbol as second, height of symbol as third)
- (optional) The first datum (type string)
- (optional) The first datum's modifying condition (tuple, svg string as first, width of symbol as second, height of symbol as third)
- (optional) The second datum (type string)
- (optional) The second datum's modifying condition (tuple, svg string as first, width of symbol as second, height of symbol as third)
- (optional) The third datum (type string)
- (optional) The third datum's material condition (tuple, svg string as first, width of symbol as second, height of symbol as third)
The ControlFrame function returns a type containing (svg string, overall width of control frame, overall height of control frame)
To get a dimension, try out the following:
import gdtsvg
ourDimension = linearDimension(point1, point2, textpoint, dimensiontext, linestyle=getStyle("visible"),
arrowstyle=getStyle("filled"), textstyle=getStyle("text")
Inputs for linear dimension are:
- point1, an (x,y) tuple with svg-coordinates, this is one of the points you would like to dimension between
- point2, an (x,y) tuple with svg-coordinates, this is the second point you would like to dimension between
- textpoint, an (x,y) tuple of svg-coordinates, this is where the text of your dimension will be
- dimensiontext, a string containing the text you want the dimension to say
- linestyle, a string containing svg (i.e. css) styles, using the getStyle function to retrieve a preset string, for styling the how the lines look
- arrowstyle, a string containing svg (i.e. css) styles, using the getStyle function to retrieve a preset string, for styling how the arrows look
- textstyle, a string containing svg (i.e. css) styles, using the getStyle function to retrieve a preset string, for styling how the text looks
With those two, you can proceed as above for displaying them on the drawing page. This module is very buggy and can be broken at any given moment, bug reports are welcome on the github page for now, or contact jcc242 on the forums if you post a bug somewhere else.
Templates
FreeCAD comes bundled with a set of default templates, but you can find more on the Drawing templates page.
Extending the Drawing Module
Some notes on the programming side of the drawing module will be added to the Drawing Documentation page. This is to help quickly understand how the drawing module works, enabling programmers to rapidly start programming for it.
Tutorials
External links