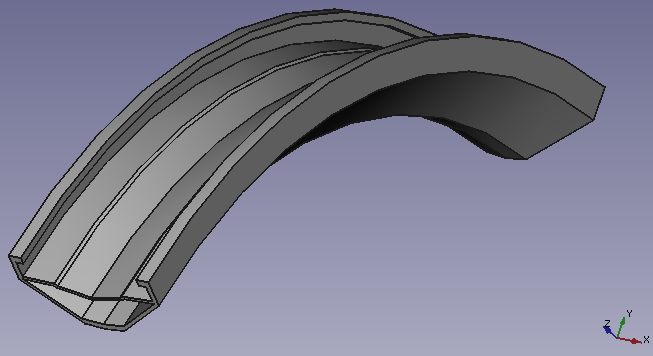
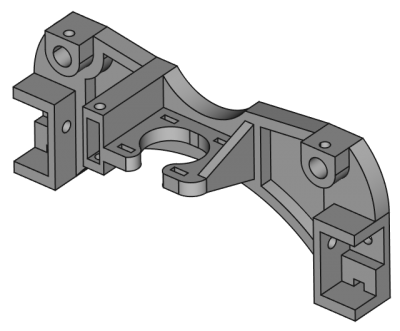
Celem Warsztatu Part Design jest dostarczenie narzędzi do modelowania złożonych brył części i jest opart o metodykę edycji Cech. Jest on głęboko połączony z Warsztatem Szkicownika.
Contents
Podstawowy przebieg pracy
Szkic jest "budulcem" do tworzenie i edycji części bryłowych. Przebieg pracy można podsumować w następujący sposób: najpierw tworzony jest szkic zawierający geometrię 2D, potem na szkicu używane jest narzędzie tworzenia brył. W tym momencie dostępnymi narzędziami są:
- Występ (Pad) który wyciąga szkic
- Kieszeń (Pocket) która tworzy kieszeń na istniejącej bryle
- Obrót (Revolve) który tworzy bryłę przez obrócenie szkicu wokół osi.
W przyszłych wydaniach planowane są kolejne narzędzia
While the Part Workbench and other FreeCAD workbenches construct models by combining shapes together, the PartDesign workbench uses features. A feature is an operation that modifies the shape of a model.
The first feature is commonly called the base feature. As more features are added to the model, each feature takes the shape of the previous one and adds or removes matter, creating linear dependencies from one feature to the next. In effect, this methodology mimics a common manufacturing process: a block is cut on one side, then on another side, holes are added, then rounds, etc.
All features are listed sequentially in the Model tree and can be edited at any time, with the last feature at the bottom representing the final part.
Narzędzia
Narzędzia Part Design znajdują się w menu Part Design pojawiającym się po załadowaniu modułu Part Design.
Zawierają one narzędzia Warsztatu Szkicownika, gdyż moduł Part Design jest od nich zależny.
Narzędzia Szkicownika
Sketcher Geometries
These are tools for creating objects.
-
 Point: Draws a point.
Point: Draws a point. -
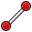 Line by 2 point: Draws a line segment from 2 points.
Line by 2 point: Draws a line segment from 2 points. -
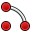 Arc: Draws an arc segment from center, radius, start angle and end angle.
Arc: Draws an arc segment from center, radius, start angle and end angle. -
 Arc by 3 Point: Draws an arc segment from two endpoints and another point on the circumference.
Arc by 3 Point: Draws an arc segment from two endpoints and another point on the circumference. -
 Circle: Draws a circle from center and radius.
Circle: Draws a circle from center and radius. -
 Circle by 3 Point : Draws a circle from three points on the circumference.
Circle by 3 Point : Draws a circle from three points on the circumference. -
 Conic sections:
Conic sections:
-
 Ellipse by center : Draws an ellipse by center point, major radius point and minor radius point. (v0.15)
Ellipse by center : Draws an ellipse by center point, major radius point and minor radius point. (v0.15) -
 Ellipse by 3 points : Draws an ellipse by major diameter (2 points) and minor radius point. (v0.15)
Ellipse by 3 points : Draws an ellipse by major diameter (2 points) and minor radius point. (v0.15) -
 Arc of ellipse : Draws an arc of ellipse by center point, major radius point, starting point and ending point. (v0.15)
Arc of ellipse : Draws an arc of ellipse by center point, major radius point, starting point and ending point. (v0.15)  Arc of hyperbola: Draws an arc of hyperbola. (v0.17)
Arc of hyperbola: Draws an arc of hyperbola. (v0.17) Arc of parabola: Draws an arc of parabola. (v0.17)
Arc of parabola: Draws an arc of parabola. (v0.17)
-
-
 Polyline (multiple-point line): Draws a line made of multiple line segments. Pressing the M key while drawing a Polyline toggles between the different polyline modes.
Polyline (multiple-point line): Draws a line made of multiple line segments. Pressing the M key while drawing a Polyline toggles between the different polyline modes. -
 Rectangle: Draws a rectangle from 2 opposite points.
Rectangle: Draws a rectangle from 2 opposite points. -
 Triangle: Draws a regular triangle inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15)
Triangle: Draws a regular triangle inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15) -
 Square: Draws a regular square inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15)
Square: Draws a regular square inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15) -
 Pentagon: Draws a regular pentagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15)
Pentagon: Draws a regular pentagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15) -
 Hexagon: Draws a regular hexagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15)
Hexagon: Draws a regular hexagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15) -
 Heptagon: Draws a regular heptagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15)
Heptagon: Draws a regular heptagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15) -
 Octagon: Draws a regular octagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15)
Octagon: Draws a regular octagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle. (v0.15) -
 Slot: Draws an oval by selecting the center of one semicircle and an endpoint of the other semicircle.
Slot: Draws an oval by selecting the center of one semicircle and an endpoint of the other semicircle. -
 Fillet: Makes a fillet between two lines joined at one point. Select both lines or click on the corner point, then activate the tool.
Fillet: Makes a fillet between two lines joined at one point. Select both lines or click on the corner point, then activate the tool. -
 Trimming: Trims a line, circle or arc with respect to the clicked point.
Trimming: Trims a line, circle or arc with respect to the clicked point. -
 External Geometry: Creates an edge linked to external geometry.
External Geometry: Creates an edge linked to external geometry. -
 Construction Mode: A construction object will be shown in blue and will not be used in a 3D geometry operation. It is only visible while editing the Sketch that contains it. Selecting existing Sketcher geometry and then clicking this tool toggles that geometry between regular and construction mode. Selecting this tool when no Sketcher geometry is selected changes the mode (regular vs. construction) in which future objects will be created.
Construction Mode: A construction object will be shown in blue and will not be used in a 3D geometry operation. It is only visible while editing the Sketch that contains it. Selecting existing Sketcher geometry and then clicking this tool toggles that geometry between regular and construction mode. Selecting this tool when no Sketcher geometry is selected changes the mode (regular vs. construction) in which future objects will be created.
Sketcher Constraints
Constraints are used to define lengths, set rules between sketch elements, and to lock the sketch along the vertical and horizontal axes. Some constraints require the Helper constraints
Not associated with numeric data
-
 Coincident: Affixes a point onto (coincident with) one or more other points.
Coincident: Affixes a point onto (coincident with) one or more other points. -
 Point On Object: Affixes a point onto another object such as a line, arc, or axis.
Point On Object: Affixes a point onto another object such as a line, arc, or axis. -
 Vertical: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true vertical orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint.
Vertical: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true vertical orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint. -
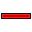 Horizontal: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true horizontal orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint.
Horizontal: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true horizontal orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint. -
 Parallel: Constrains two or more lines parallel to one another.
Parallel: Constrains two or more lines parallel to one another. -
 Perpendicular: Constrains two lines perpendicular to one another, or constrains a line perpendicular to an arc endpoint.
Perpendicular: Constrains two lines perpendicular to one another, or constrains a line perpendicular to an arc endpoint. -
 Tangent: Creates a tangent constraint between two selected entities, or a co-linear constraint between two line segments. A line segment does not have to lie directly on an arc or circle to be constrained tangent to that arc or circle.
Tangent: Creates a tangent constraint between two selected entities, or a co-linear constraint between two line segments. A line segment does not have to lie directly on an arc or circle to be constrained tangent to that arc or circle. -
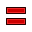 Equal Length: Constrains two selected entities equal to one another. If used on circles or arcs their radii will be set equal.
Equal Length: Constrains two selected entities equal to one another. If used on circles or arcs their radii will be set equal. -
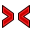 Symmetric: Constrains two points symmetrically about a line, or constrains the first two selected points symmetrically about a third selected point.
Symmetric: Constrains two points symmetrically about a line, or constrains the first two selected points symmetrically about a third selected point. -
 Constrain Block: v 0.17 Basically allows to block a geometric element in place with a single constraint. It should be particularly useful to work with B-Splines. See https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=26572
Constrain Block: v 0.17 Basically allows to block a geometric element in place with a single constraint. It should be particularly useful to work with B-Splines. See https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=26572
Associated with numeric data
For these constraints you can use the expressions. The data may be taken from a spreadsheet.
-
 Lock: Constrains the selected item by setting vertical and horizontal distances relative to the origin, thereby locking the location of that item. These constraint distances can be edited later.
Lock: Constrains the selected item by setting vertical and horizontal distances relative to the origin, thereby locking the location of that item. These constraint distances can be edited later. -
 Horizontal Distance: Fixes the horizontal distance between two points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin.
Horizontal Distance: Fixes the horizontal distance between two points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin. -
 Vertical Distance: Fixes the vertical distance between 2 points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin.
Vertical Distance: Fixes the vertical distance between 2 points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin. -
 Length: Defines the distance of a selected line by constraining its length, or defines the distance between two points by constraining the distance between them.
Length: Defines the distance of a selected line by constraining its length, or defines the distance between two points by constraining the distance between them. -
 Radius: Defines the radius of a selected arc or circle by constraining the radius.
Radius: Defines the radius of a selected arc or circle by constraining the radius. -
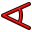 Internal Angle: Defines the internal angle between two selected lines.
Internal Angle: Defines the internal angle between two selected lines. -
 Snell's Law: Constrains two lines to obey a refraction law to simulate the light going through an interface. (v 0.15)
Snell's Law: Constrains two lines to obey a refraction law to simulate the light going through an interface. (v 0.15) -
 Internal Alignment: Aligns selected elements to selected shape (e.g. a line to become major axis of an ellipse).
Internal Alignment: Aligns selected elements to selected shape (e.g. a line to become major axis of an ellipse).
-
 Toggle Constraint: Toggles the toolbar or the selected constraints to/from reference mode. v0.16
Toggle Constraint: Toggles the toolbar or the selected constraints to/from reference mode. v0.16
Other
-
 New sketch: Creates a new sketch on a selected face or plane. If no face is selected while this tool is executed the user is prompted to select a plane from a pop-up window.
New sketch: Creates a new sketch on a selected face or plane. If no face is selected while this tool is executed the user is prompted to select a plane from a pop-up window.
-
 Edit sketch: Edit the selected Sketch.
Edit sketch: Edit the selected Sketch.
-
 Leave sketch: Leave the Sketch editing mode.
Leave sketch: Leave the Sketch editing mode.
-
 View sketch: Sets the model view perpendicular to the sketch plane.
View sketch: Sets the model view perpendicular to the sketch plane.
-
 Map sketch to face: Maps a sketch to the previously selected face of a solid.
Map sketch to face: Maps a sketch to the previously selected face of a solid.
- Reorient sketch : Allows you to change the position of a sketch
- Validate sketch: It allows you to check if there are in the tolerance of different points and to match them.
-
 Merge sketches: Merge two or more sketches. [v 0.15]
Merge sketches: Merge two or more sketches. [v 0.15]
-
 Mirror sketch: Mirror a sketch along the x-axis, the y-axis or the origin [v 0.16]
Mirror sketch: Mirror a sketch along the x-axis, the y-axis or the origin [v 0.16]
-
 Close Shape: Creates a closed shape by applying coincident constraints to endpoints [v 0.15]
Close Shape: Creates a closed shape by applying coincident constraints to endpoints [v 0.15]
-
 Connect Edges: Connect sketcher elements by applying coincident constraints to endpoints [v 0.15]
Connect Edges: Connect sketcher elements by applying coincident constraints to endpoints [v 0.15]
-
 Select Constraints: Selects the constraints of a sketcher element [v 0.15]
Select Constraints: Selects the constraints of a sketcher element [v 0.15]
-
 Select Origin: Selects the origin of a sketch [v 0.15]
Select Origin: Selects the origin of a sketch [v 0.15]
-
 Select Vertical Axis: Selects the vertical axis of a sketch [v 0.15]
Select Vertical Axis: Selects the vertical axis of a sketch [v 0.15]
-
 Select Horizontal Axis: Selects the horizontal axis of a sketch [v 0.15]
Select Horizontal Axis: Selects the horizontal axis of a sketch [v 0.15]
-
 Select Redundant Constraints: Selects redundant constraints of a sketch [v 0.15]
Select Redundant Constraints: Selects redundant constraints of a sketch [v 0.15]
-
 Select Conflicting Constraints: Selects conflicting constraints of a sketch [v 0.15]
Select Conflicting Constraints: Selects conflicting constraints of a sketch [v 0.15]
-
 Select Elements Associated with constraints: Select sketcher elements associated with constraints [v 0.15]
Select Elements Associated with constraints: Select sketcher elements associated with constraints [v 0.15]
-
 Show/Hide internal geometry: Recreates missing/deletes unneeded geometry aligned to internal geometry of a selected element (applicable only to ellipse so far). [v 0.15]
Show/Hide internal geometry: Recreates missing/deletes unneeded geometry aligned to internal geometry of a selected element (applicable only to ellipse so far). [v 0.15]
-
 Symmetry: Copies a sketcher element symmetrical to a chosen line [v 0.16]
Symmetry: Copies a sketcher element symmetrical to a chosen line [v 0.16]
-
 Clone: Clones a sketcher element [v 0.16]
Clone: Clones a sketcher element [v 0.16]
-
 Copy: Copies a sketcher element [v 0.16]
Copy: Copies a sketcher element [v 0.16]
-
 Rectangular Array: Creates an array of selected sketcher elements [v 0.16]
Rectangular Array: Creates an array of selected sketcher elements [v 0.16]
-
 Switch Virtual Space: v 0.17 Allows you to "hide" constraints and make them visible again. See https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=26614
Switch Virtual Space: v 0.17 Allows you to "hide" constraints and make them visible again. See https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=26614
Preferences
-
 Preferences...: Preferences disposable in Sketcher Tools.
Preferences...: Preferences disposable in Sketcher Tools.
Narzędzia Part Design
Construction tools
These are tools for creating solid objects or removing material from an existing solid object.
-
 Pad: Extrudes a solid object from a selected sketch.
Pad: Extrudes a solid object from a selected sketch. -
 Pocket: Creates a pocket from a selected sketch. The sketch must be mapped to an existing solid object's face.
Pocket: Creates a pocket from a selected sketch. The sketch must be mapped to an existing solid object's face. -
 Revolution: Creates a solid by revolving a sketch around an axis. The sketch must be a closed profile to get a solid object.
Revolution: Creates a solid by revolving a sketch around an axis. The sketch must be a closed profile to get a solid object. -
 Groove: Creates a groove by revolving a sketch around an axis. The sketch must be mapped to an existing solid object's face.
Groove: Creates a groove by revolving a sketch around an axis. The sketch must be mapped to an existing solid object's face.
Modification tools
These are tools for modifying existing objects. They will allow you to choose which object to modify.
-
 Fillet: Fillets (rounds) edges of an object.
Fillet: Fillets (rounds) edges of an object. -
 Chamfer: Chamfers edges of an object.
Chamfer: Chamfers edges of an object. -
 Draft: Applies angular draft to faces of an object.
Draft: Applies angular draft to faces of an object.
Transformation tools
These are tools for transforming existing features. They will allow you to choose which features to transform.
-
 Mirrored: Mirrors features on a plane or face.
Mirrored: Mirrors features on a plane or face. -
 Linear Pattern: Creates a linear pattern of features.
Linear Pattern: Creates a linear pattern of features. -
 Polar Pattern: Creates a polar pattern of features.
Polar Pattern: Creates a polar pattern of features. -
 Scaled: Scales features to a different size.
Scaled: Scales features to a different size. -
 MultiTransform: Allows creating a pattern with any combination of the other transformations.
MultiTransform: Allows creating a pattern with any combination of the other transformations.
Boolean tools
These are tools for create boolean operation with two or more bodies
-
 Boolean: Creates boolean operation with two or more bodies
Boolean: Creates boolean operation with two or more bodies
- Procedural: can be said of features that are not based on sketches, like the transformation and dress-up features.
Body
The Body is a container that groups a sequence of features forming a single contiguous solid.
What is a single contiguous solid? It is an object like a casting or something machined from a single block of metal. If the object involves nails, screws, glue or welding, it is not a single contiguous solid. As a practical example, a wooden chair would be made of multiple bodies, with one for each of its sub-components (legs, slats, seat, etc).
Body Visibility Management
A body will present by default its most recent feature to the outside. This feature is defined by default as the tip. A good analogy is the expression the tip of the iceberg: only the tip is visible above the water, most of the iceberg's mass (the other features) is hidden. As a new feature is added to the body, visibility of the previous feature is turned off, and the new feature becomes the tip.
There can only be one feature visible at a time. It is possible to toggle the visibility of any feature in the body, by selecting it in the Model tree and pressing the spacebar, in effect going back in the history of the body.
Body Origin
The body has an Origin which consists of reference planes (XY, XZ, YZ) and axes (X, Y, Z) that can be used by sketches and features. Sketches can be attached to Origin planes, and they no longer need to be mapped to planar faces for features based on them to be added or subtracted from the model.
Moving and Reordering Objects
It is possible to temporarily redefine the tip to a feature in the middle of the Body tree to insert new objects (features, sketches or datum geometry). It is also possible to reorder features under a Body, or to move them to a different Body. Select the object and right-click to get a contextual menu that will offer both options. The operation may be prevented if the object has dependencies in the source Body, such as being attached to a face. To move a sketch to another Body, it should not contain links to external geometry.
Datum Geometry
Datum geometry consists of custom planes, lines, points or externally linked shapes. They can be created for use as reference by sketches and features. There is a multitude of attachment possibilities for datums.
Cross-referencing
It is possible to cross-reference elements from a body in another body via datums. For example the datum shape binder allows to copy over faces from a body as reference in another one. This should make it easy to build a box with fitting cover in two different bodies. FreeCAD helps you to not accidentally link to other bodies and queries your intent.
Attachment
Object attachment is not a specific PartDesign tool, but rather a Part utility introduced in v0.17 that can be found in the Part menu. It is heavily used in the PartDesign workbench to attach sketches and reference geometry to the standard planes and axes of the Body. Very extensive ways of creating datum points, lines and planes are available. Optional attachment offset parameters make this tool very versatile.
More info can be found in the Attachment page.
Advice for creating stable models
The idea of parametric modeling implies that you can change the values of certain parameters and subsequent steps are changed according to the new values. However, when severe changes are made, the model can break. Compared to previous FreeCAD versions breaking can be minimized when you respect the following design principles:
- Basically, you need to stop mapping sketches to faces - entirely! Place your sketches on standard planes, or on custom datum planes.
- When creating datum geometry, do not base it on the part topology, base it on standard planes/axes and/or sketches.
- Use a "master sketch". That is a preferably not too complicated sketch which contains basic geometric elements of your model. These elements can be referenced when modeling subsequent features. Such a master sketch will often be the first sketch in the Body but it doesn't have to be; in fact you don't even have to use it at all for anything else but being referenced.
- If you inevitably have to reference an intermediate feature, e.g. the result of a thickness operation, use the first reference possible in the list of subsequent features where the referenced geometric element occurs. From FreeCAD 0.17 on you don't have to use the latest feature. If you take an early feature as reference, all changes to intermediate steps won't break your model. And again it is better to reference a sketch than edges and vertices of a solid
The Tools
The Part Design tools are all located in the Part Design menu and the PartDesign toolbar that appear when you load the Part Design workbench.
Structure tools
These are tools to organize the Model tree.
-
 Part: adds a new Part container in the active document and makes it active.
Part: adds a new Part container in the active document and makes it active. -
Group: adds a Group in the active document's Model tree.
Part Design Helper tools
 Create body: Creates a Body in the active document and makes it active.
Create body: Creates a Body in the active document and makes it active.
 Create sketch: creates a new sketch on a selected face or plane. If no face is selected while this tool is executed, the user is prompted to select a plane from the Tasks panel. The interface then switches to the Sketcher_Workbench in sketch editing mode.
Create sketch: creates a new sketch on a selected face or plane. If no face is selected while this tool is executed, the user is prompted to select a plane from the Tasks panel. The interface then switches to the Sketcher_Workbench in sketch editing mode.
-
 Edit sketch: Edit the selected Sketch.
Edit sketch: Edit the selected Sketch.
-
 Map sketch to face: Maps a sketch to a previously selected plane or a face of the active body.
Map sketch to face: Maps a sketch to a previously selected plane or a face of the active body.
Part Design Modeling tools
Datum tools
 Create a datum point: creates a datum point in the active body.
Create a datum point: creates a datum point in the active body.
 Create a datum line: creates a datum line in the active body.
Create a datum line: creates a datum line in the active body.
 Create a datum plane: creates a datum plane in the active body.
Create a datum plane: creates a datum plane in the active body.
 Create a shape binder: creates a shape binder in the active body.
Create a shape binder: creates a shape binder in the active body.
 Create a clone: creates a clone of the selected body.
Create a clone: creates a clone of the selected body.
Additive tools
These are tools for creating base features or adding material to an existing solid body.
-
 Pad: extrudes a solid from a selected sketch.
Pad: extrudes a solid from a selected sketch.
-
 Revolution: creates a solid by revolving a sketch around an axis. The sketch must form a closed profile.
Revolution: creates a solid by revolving a sketch around an axis. The sketch must form a closed profile.
 Additive loft: creates a solid by making a transition between two or more sketches.
Additive loft: creates a solid by making a transition between two or more sketches.
 Additive pipe: creates a solid by sweeping one or more sketches along an open or closed path.
Additive pipe: creates a solid by sweeping one or more sketches along an open or closed path.
- Create an additive primitive: adds an additive primitive to the active body.
 Additive box: creates an additive box.
Additive box: creates an additive box.
 Additive cone: creates an additive cone.
Additive cone: creates an additive cone.
 Additive cylinder: creates an additive cylinder.
Additive cylinder: creates an additive cylinder.
 Additive ellipsoid: creates an additive ellipsoid.
Additive ellipsoid: creates an additive ellipsoid.
 Additive prism: creates an additive prism.
Additive prism: creates an additive prism.
 Additive sphere: creates an additive sphere.
Additive sphere: creates an additive sphere.
 Additive torus: creates an additive torus.
Additive torus: creates an additive torus.
 Additive wedge: creates an additive wedge.
Additive wedge: creates an additive wedge.
Subtractive tools
These are tools for subtracting material from an existing body.
-
 Pocket: creates a pocket from a selected sketch.
Pocket: creates a pocket from a selected sketch.
-
 Hole: creates a hole feature from a selected sketch. The sketch must contain one or multiple circles.
Hole: creates a hole feature from a selected sketch. The sketch must contain one or multiple circles.
-
 Groove: creates a groove by revolving a sketch around an axis.
Groove: creates a groove by revolving a sketch around an axis.
 Subtractive loft: creates a solid shape by making a transition between two or more sketches and subtracts it from the active body.
Subtractive loft: creates a solid shape by making a transition between two or more sketches and subtracts it from the active body.
 Subtractive pipe: creates a solid shape by sweeping one or more sketches along an open or closed path and subtracts it from the active body.
Subtractive pipe: creates a solid shape by sweeping one or more sketches along an open or closed path and subtracts it from the active body.
- Create a subtractive primitive: adds a subtractive primitive to the active body.
 Subtractive box: adds a subtractive box to the active body.
Subtractive box: adds a subtractive box to the active body.
 Subtractive cone: adds a subtractive cone to the active body.
Subtractive cone: adds a subtractive cone to the active body.
 Subtractive cylinder: adds a subtractive cylinder to the active body.
Subtractive cylinder: adds a subtractive cylinder to the active body.
 Subtractive ellipsoid: adds a subtractive ellipsoid to the active body.
Subtractive ellipsoid: adds a subtractive ellipsoid to the active body.
 Subtractive prism: adds a subtractive prism to the active body.
Subtractive prism: adds a subtractive prism to the active body.
 Subtractive sphere: adds a subtractive sphere to the active body.
Subtractive sphere: adds a subtractive sphere to the active body.
 Subtractive torus: adds a subtractive torus to the active body.
Subtractive torus: adds a subtractive torus to the active body.
 Subtractive wedge: adds a subtractive wedge to the active body.
Subtractive wedge: adds a subtractive wedge to the active body.
Transformation tools
These are tools for transforming existing features. They will allow you to choose which features to transform.
-
 Mirrored: mirrors one or more features on a plane or face.
Mirrored: mirrors one or more features on a plane or face.
-
 Linear Pattern: creates a linear pattern based on one or more features.
Linear Pattern: creates a linear pattern based on one or more features.
-
 Polar Pattern: creates a polar pattern of one or more features.
Polar Pattern: creates a polar pattern of one or more features.
-
 Create MultiTransform: creates a pattern with any combination of the other transformations.
Create MultiTransform: creates a pattern with any combination of the other transformations.
Dress-up tools
These tools apply a treatment to the selected edges or faces.
 Fillet: fillets (rounds) edges of the active body.
Fillet: fillets (rounds) edges of the active body.
 Chamfer: chamfers edges of the active body.
Chamfer: chamfers edges of the active body.
 Draft: applies and angular draft to faces of the active body.
Draft: applies and angular draft to faces of the active body.
 Thickness: creates a thick shell from the active body and opens selected face(s).
Thickness: creates a thick shell from the active body and opens selected face(s).
Boolean
 Boolean operation: imports one or more Bodies or PartDesign Clones into the active body and applies a Boolean operation.
Boolean operation: imports one or more Bodies or PartDesign Clones into the active body and applies a Boolean operation.
Extras
Some additional functionality found in the Part Design menu:
- Migrate: migrates files created with older FreeCAD versions. If the file is pure PartDesign feature-based, migration should succeed. If the file contains mixed Part/Part Design/Draft objects, the conversion will most likely fail.
-
 Shaft design wizard: Generates a shaft from a table of values and allows to analyze forces and moments. The shaft is made with a revolved sketch that can be edited.
Shaft design wizard: Generates a shaft from a table of values and allows to analyze forces and moments. The shaft is made with a revolved sketch that can be edited.
-
 Involute gear: creates an involute gear profile that can be used by a Pad.
Involute gear: creates an involute gear profile that can be used by a Pad.
Contextual Menu tools
 Set tip: redefines the tip, which is the feature exposed outside of the Body.
Set tip: redefines the tip, which is the feature exposed outside of the Body.
- Move object to other body: moves the selected sketch, datum geometry or feature to another Body.
- Move object after other object: allows reordering of the Body tree by moving the selected sketch, datum geometry or feature to another position in the list of features.
Preferences
 Preferences...: Preferences disposable in PartDesign Tools.
Preferences...: Preferences disposable in PartDesign Tools.
Tutorials
- Creating a simple part with PartDesign v0.17
- Basic Part Design Tutorial 017
- PartDesign Bearingholder Tutorial I (needs updating)
- PartDesign Bearingholder Tutorial II (needs updating)
Links
- What's new in PartDesign Next
- Updated PartDesign workflow
- FC v0.17dev: Part Design Next Usecases and Best practices
- Sandbox:Part Design Next